这篇文章介绍了一个启发于帝国竞争的算法。和很多的其它进化算法一样,这个算法从一个初始的种群开始。Population individuals called country are in two types: colonies(殖民地) and imperialists(帝国主义) that all together form some empires(帝国). Imperialistic competition among these empires forms the basis of the proposed evolutionary algorithm. 在竞争的过程中,弱小的帝国被瓦解而强大的帝国获得它们的殖民地,最后只剩下一个帝国,理论上最后帝国中所有的国家都有一致性的cost(这要求目标函数连续) ,这个算法对于很多优化问题都有很好的效果。
Introduction
像遗传算法模拟了自然的进化过程;模拟退火法模拟了锻造的过程,先加热到融化的温度以上然后逐步冷却,获得最小的能量概率分布;蚁群算法通过模拟蚂蚁的觅食行为;还有PSO算法等等。这里提出的帝国竞争算法也是模拟了实际的过程,重点介绍帝国竞争。
Proposed algorithm
Generating Initial Empires
我们的目标是找到最优解。我们生成一个向量用来表示自变量,在遗传算法里面称为染色体,我们这里称为国家(country), 如果这是一个$N_{var}-dimensional$ optimization problem, a country is a $1\times N_{var}$ array. This array is defined by:
the variable values in the country are represented as floating point numbers. The cost of a country is found by evaluating the cost function $f$ at variables($p_1,p_2,p_3,…,p_{N_{var}}$).Then
We generate the initial population of size $N_{pop}$. We select $N_{imp}$ of the most powerful countries to form the empires. The remaining $N_{col}$ of the population will be the colonies each of which belongs to an empire. Then we have two types of countries: imperialist and colony.
To form the initial empires, we divide the colonies among imperialists based on their power. That is the initial number of colonies of an empire should be directly proportionate to its power. To divide the colonies among imperialists proportionally,we define the normalized cost of an imperialist by
其中$c_n$ 是第n个统治国(nth imperialist) 的cost,都减去了所有国家中最大的cost,$C_n$ 是其normalized cost. 然后我们定义其normalized power by
从另外一个角度看,这个正则化后的影响力(normalized power)表示了殖民地划分的比例。Then the initial number of colonies of an empire will be
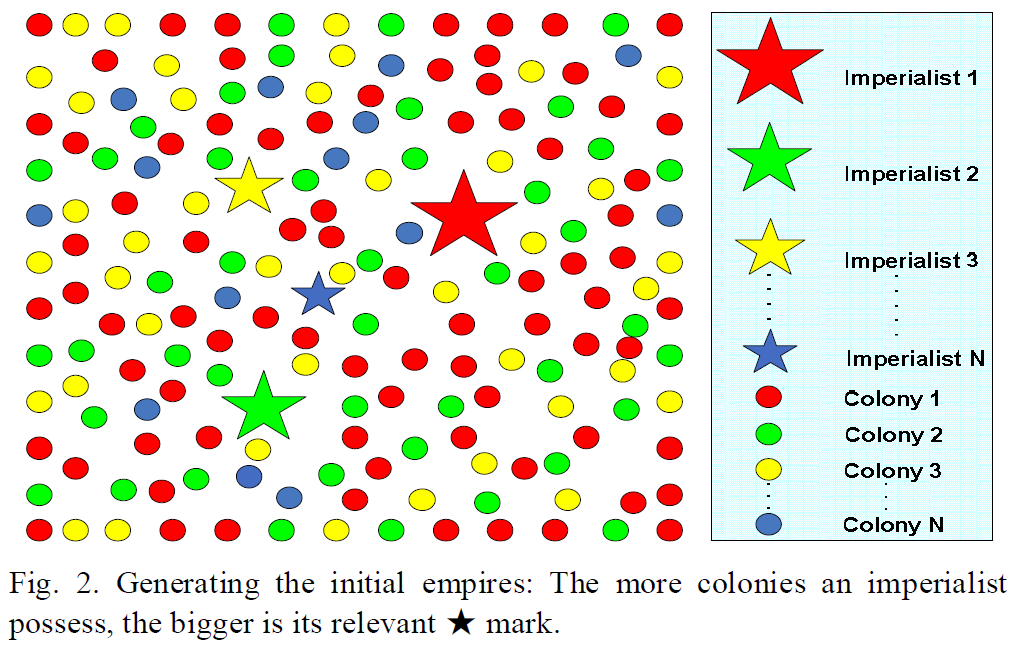
然后我们随机选择$N.C_n$ 个殖民地给每个帝国,影响力越大的帝国殖民地也越多,下图是一个示例:
Moving the colonies toward the imperialist
统治国开始整治殖民地,使殖民地变得更好。我们通过殖民地向着统治国的移动来达到这点。下图展示了这个过程,其中移动了$x$ 个单元长度,起始于灰色位置落在深色位置。
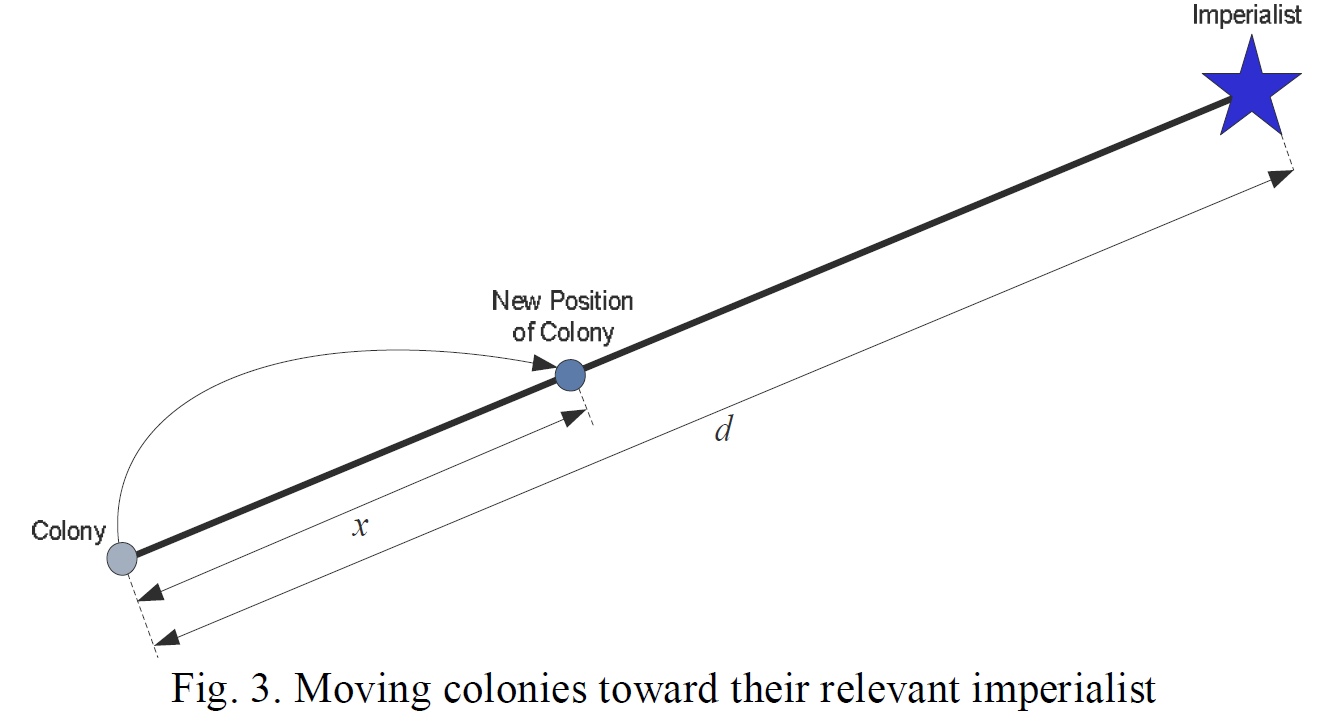
其中$x$ 是一个均匀分布的随机数:
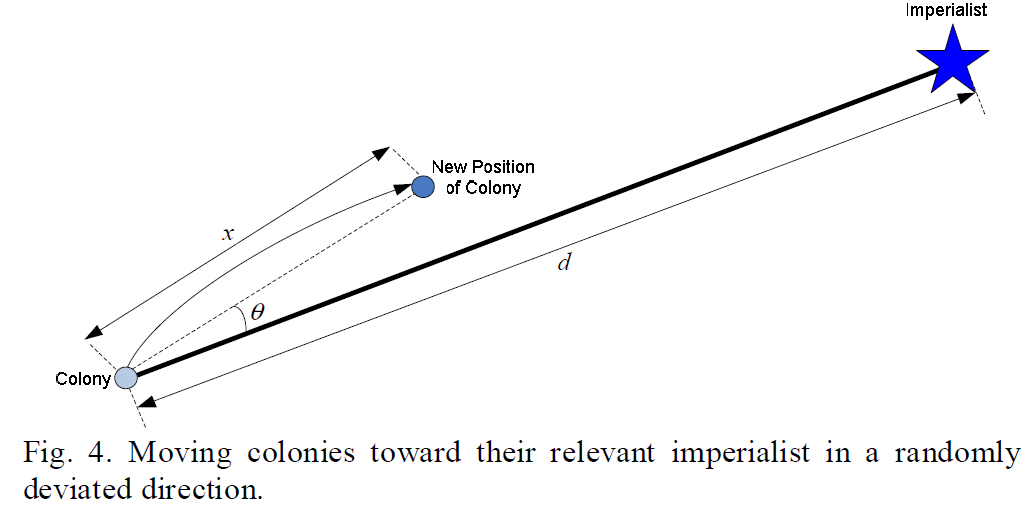
其中$\beta$ 是一个大于1的数,这样殖民地可以靠近统治国from both sides. 为了搜索不同的点,我们在方位上加入了一定的随机扰动$\theta$ :
$\gamma$ 是一个参数表示偏离原始方位的度。最常用的参数为$\beta=2\;\;and\;\;\gamma=\pi/4$ ,这样的收敛性比较好。下图为最后的搜索示意图:
Update Imperialist
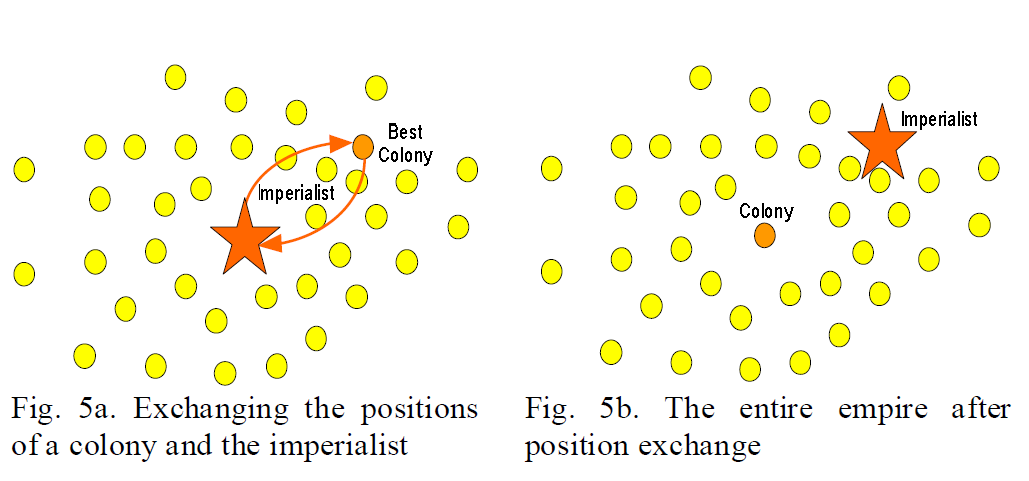
搜索的过程中殖民地相比于统治国可能获得了更好的cost,那么就要交换两者的位置,然后后面的搜索都基于新的统治国展开,下图展示了这个过程:
Total Power of an Empire
Total power of an empire is mainly affected by the power of imperialist country. But the power of the colonies of an empire has an effect, albeit negligible, on the total power of that empire. We modeled this fact by define the total cost by
we have used the value 0.01 for $\xi$ in most of our implementation. (对于连续目标函数来说采用平均值还是不错的,可以延缓结束进程,获得更好的解)
Imperialistic Competition
最差的帝国被强大的帝国吞并一部分。通常我们选择最差的帝国中最差的殖民地,按照每个帝国的影响力选择性给一个更加强大的帝国,如图:
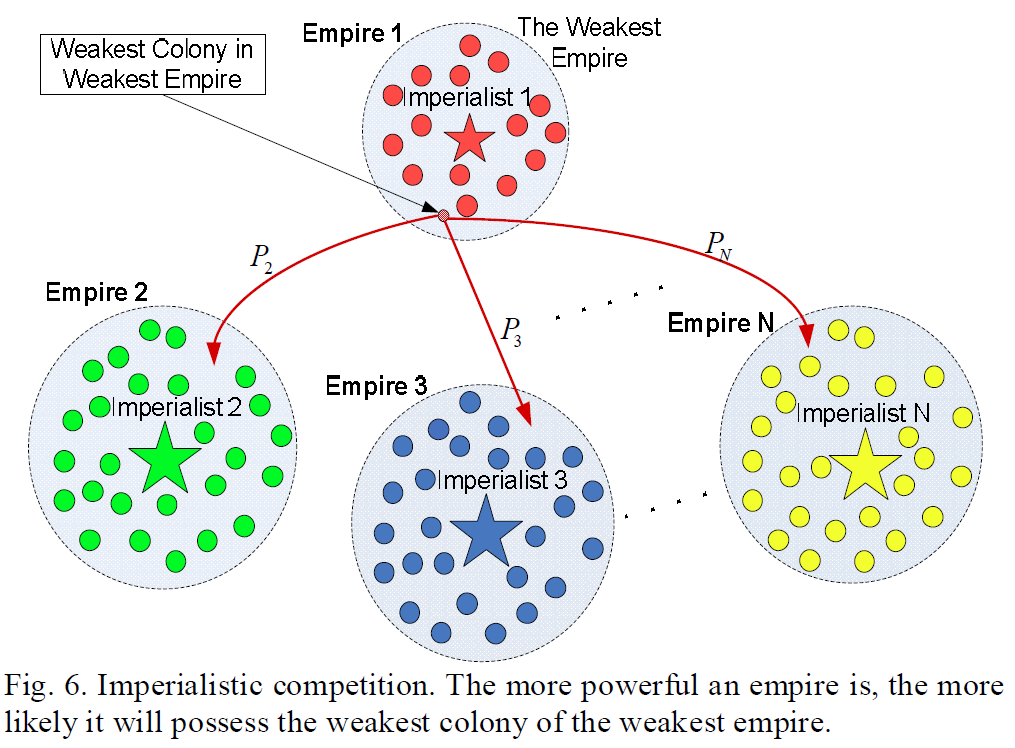
To start the competition, first, we find the possession probability of each empire based on its total power. The normalized total cost is simply obtained by
Having the normalized total cost, the possession probability of each empire is given by
we form the vector P as
Then we create a vector with same shape:
Then we form vector D by $D=P-R$, referring to D we will hand the mentioned colonies to an empire whose relevant index in D is maximum.
Eliminating the powerless Empires
这个可以采用不同的规则,我们采用的规则是这个帝国解体当且仅当其失去了所有的殖民地。
Convergence
当只留存了一个帝国,并且帝国内的国家均一(要达到均一,就是所有帝国cost基本一致,一般情况下目标函数要求连续)的情况下,算法终止。
Code
Here is the pseudo code of algorithm:
