人工智能开源的发展力是有目共睹的,现在我们正在以前所未有的速度在扩展智能算法应用的领域。如果说现在发布一条新闻:世界上首对人机情侣领取结婚证。我想我内心竟然毫无波动甚至有点想笑。深度学习一个大的跨越就是DeepMind发布的AlphaGo Zero,它证明了在没有人类先验知识的条件下,人工智能可以达到人类的水准之上。一起看看吧:
监督学习可以copy人类专家的思维决策,但是这个成本很大。所以增强学习是很有必要的,理论上增强学习可以超越人类的技能并能在人类缺乏的领域工作。这个工作极富挑战性,就比如围棋,需要一个精确而圆滑的前瞻,才能在广阔的搜索域取得效果。
Features
AlphaGo Zero与前代不同之处主要有以下几个方面:
仅仅通过自对弈的增强学习,从随机策略开始,没有使用人类经验
只用了黑白子的信息作为输入特征
只使用了单个神经网络同时输出策略和价值
使用了一个更加简洁的搜索树,没有rollout操作
RL of AlphaGo Zero
Our new method uses a deep neural network $f_\theta$ with parameters θ. This neural network takes as an input the raw board representation s of the position and its history, and outputs both move probabilities and a value, $(p,v)=f_\theta(s)$. 其中向量p表示了每一个move被选择的概率(包括pass), $p_a=Pr(a\mid s)$ . 标量v表示当前玩家在当前状态s下赢盘的概率。这个网络把策略网络和价值网络包含在一起,同时加入了BN操作和残差单元。
我们开创了一个新颖的增强学习算法:In each position s, an MCTS search is executed, guided by the neural network $f_\theta$. The MCTS search outputs probabilities π of playing each move. These search probabilities usually select much stronger moves than the raw move probabilities p of the neural network $f_\theta(s)$. 我们可以把MCTS看作一个强大的策略增强算子,Self-play with search—using the improved MCTS-based policy to select each move, then using the game winner z as a sample of the value-可以看成一个强大的策略评估算子。the neural network’s parameters are updated to make the move probabilities and value $(p,v)=f_\theta(s)$ more closely match the improved search probabilities and self-play winner (π, z); these new parameters are used in the next iteration of self-play to make the search even stronger.
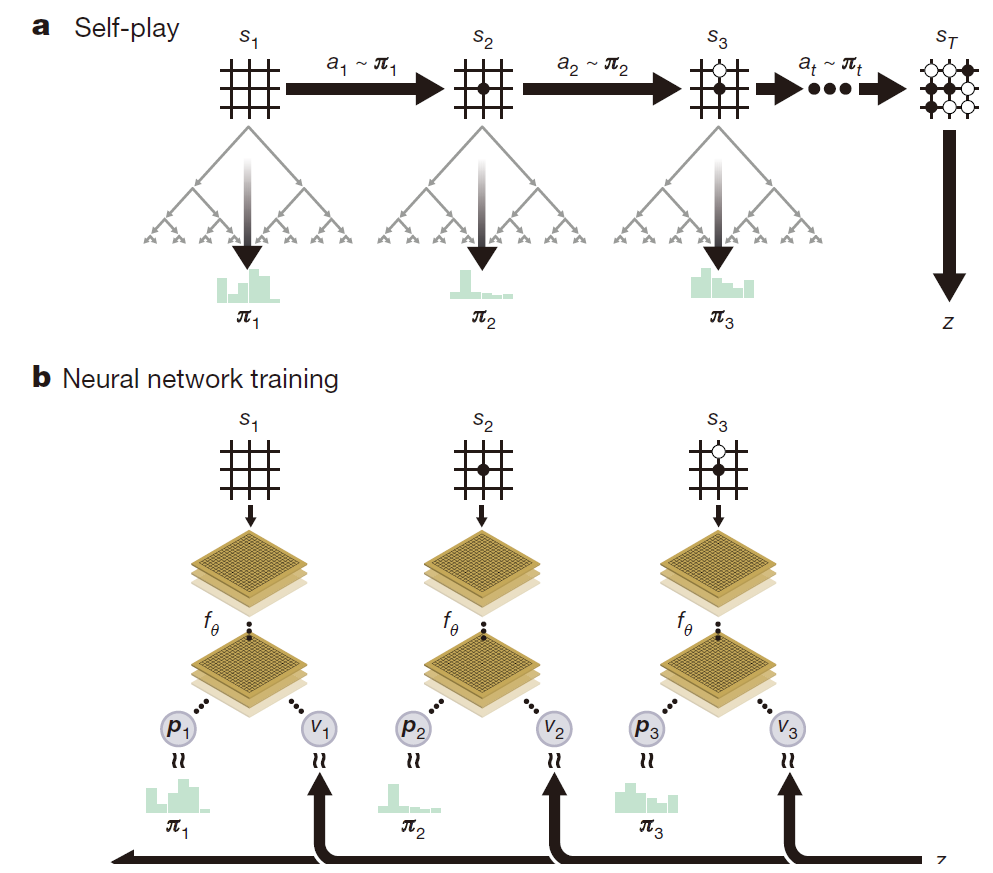
a, The program plays a game $s_1,s_2,…,s_T$ against itself. In each position $s_t$, **an MCTS $\alpha_\theta$ is executed using the latest neural network $f_\theta$ **. Moves are selected according to the search probabilities computed by the MCTS, $a_t\sim \pi_t$. The terminal position $s_T$ is scored according to the rules of the game to compute the game winner z.
b,The neural network parameters θ are updated to maximize the similarity of the policy vector $p_t$ the search probabilities $\pi_t$, and to minimize the error between the predicted winner $v_t$ and the game winner z .
MCTS使用$f_\theta$ 指导仿真。每一个edge (s,a) 包含了先验概率P(s,a), 访问次数N(s,a), 动作价值Q(s,a). 每次仿真都是从根状态开始,选择动作以最大化上置信区间 $Q(s,a)+u(s,a) $, where $u(s_t,a)\propto\frac{P(s,a)}{1+N(s,a)}$ ,直到达到状态s’, 然后扩展状态 s’ , 利用网络(仅仅一次)产生所有的动作先验概率和状态s’的价值评估:
每一个仿真经过的节点 edge (s,a) 都要经过如下更新:
MCTS 可以看出一个自对弈算法, 给出神经网络参数$\theta$ 和一个根状态 s,计算每一个动作的搜索概率, $\pi=\alpha_\theta(s)$, proportional to the exponentiated visit count for each move, $\pi_a\propto N(s,a)^{1/\tau}$, where τ is a temperature parameter.
这个自对弈增强网络每次通过MCTS来选择动作,首先初始化网络参数为$\theta_0$, 在每一次迭代($i\geq1$), 自对弈都会产生。在time-step t,MCTS search $\pi_t=\alpha_{\theta_{i-1}}(s_t)$ is executed using the previous iteration of neural network $f_{\theta_{i-1}}$ and a move is played by sampling the search probabilities $\pi_t$. 当双方都pass,或者达到步数限制,或者一方价值估计达到终止阈值的时候,游戏终止(记为time-step T)。然后给游戏打分给一个最终的回报:$r_T\in {-1,+1}$. The data for each time-step t is stored as $(s_t,\pi_t,z_t)$, where $z_t=\pm r_T$ is the game winner from the perspective of the current player at step t. 同步地,新的网络参数$\theta_i$ 通过上几次自对弈的所有time-step数据随机采样$(s,\pi,z)$ 进行训练。the parameters θ are adjusted by gradient descent on a loss function $l$ that sums over the mean-squared error and cross-entropy losses, respectively:
其中c是L2正则项,避免过拟合。
MCTS的示意图如下:
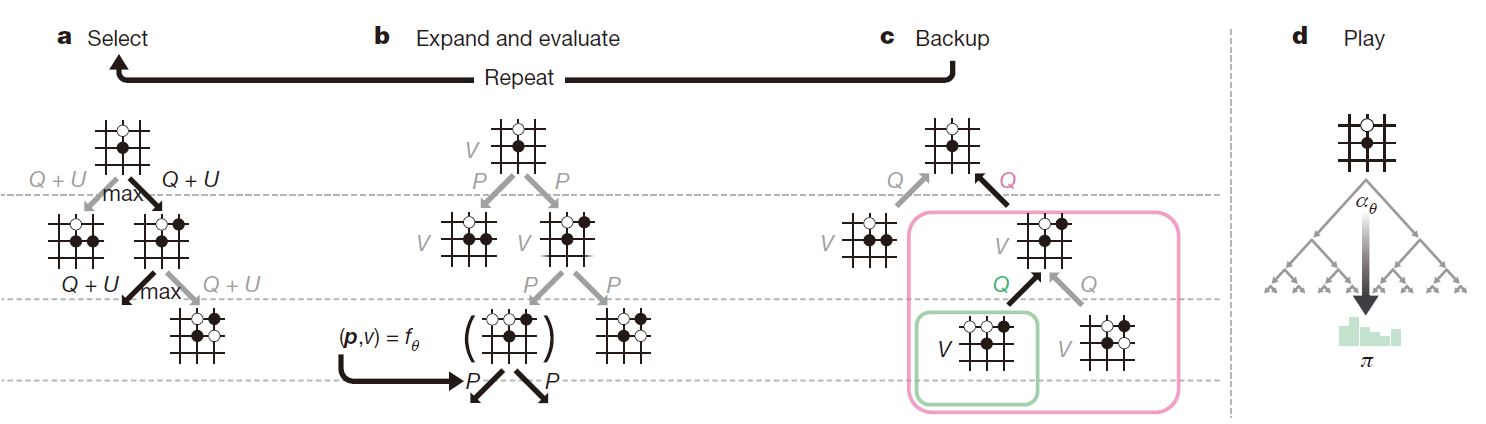
Note: Action value Q is updated to track the mean of all evaluations V in the subtree below that action.
Empirical(经验) analysis of training
Over the course of training, 4.9 million games of self-play were generated, using 1,600 simulations for each MCTS. Parameters were updated from 700,000 mini-batches of 2,048 positions. The neural network contained 20 residual blocks.
Next figure shows the performance of AlphaGo Zero during self-play reinforcement learning, as a function of training time, on an Elo scale:
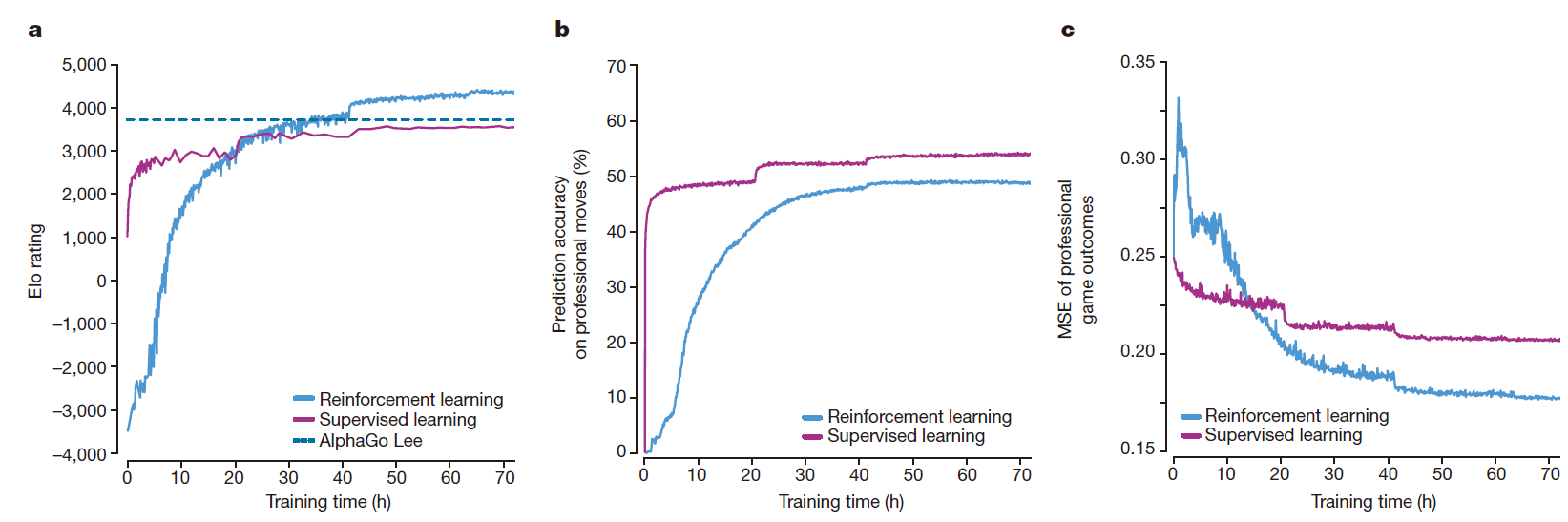
学习的过程很顺畅,没有前人提到的灾难性震荡。 Surprisingly, AlphaGo Zero outperformed AlphaGo Lee after just 36 h. In comparison, AlphaGo Lee was trained over several months.
为了凸显出自学习的优点,我们训练了一个结构一样的SL网络,对专家下子进行学习。SL网络一开始取得更好的效果,并且能更好预测人类专家的下子。但是,尽管SL网络有更高的预测精度,RL网络表现更好,在仅仅24h内就超过了SL网络,说明RL学习到了与人类下子不一样的策略。
而为了区分网络结构和算法的贡献度,我们设计了多个网络进行对比:策略网络与价值网络分开, as were used in AlphaGo Lee, or 联合动作价值网络, as used in AlphaGo Zero; and using either the 纯卷积网络结构 from AlphaGo Lee or the 残差网络结构 from AlphaGo Zero. 每个网络都优化相同的目标函数, 用同一个数据(通过训练了72小时的 AlphaGo Zero 产生的自对弈数据), 结果如下图:
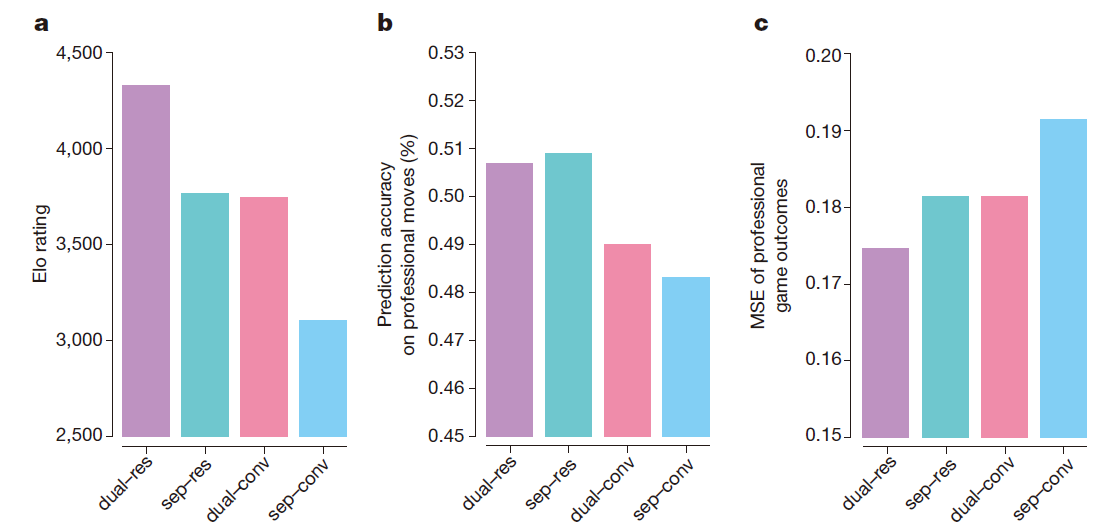
后面两张图是关于预测精度和MSE(mean square error), 数据集采用GoKifu dataset。利用残差单元更加准确,实现了更小的预测误差并达到了接近600Elo的更好表现;联合了动作和价值网络些许降低了预测的精度,但是同样降低了预测误差,实现了另外600Elo的表现提升。This is partly due to improved computational efficiency, but more importantly the dual objective regularizes the network to a common representation that supports multiple use cases.
AlphaGo Zero 不仅学习到了人类专家的经验,而且好学习到了超人类的经验。而这些经验都是通过最初的简单规则引导学习的,充分体现了深度神经网络的高效性。其中令人惊奇的是:“征子”这种人类棋手重视的规则是在训练后期才逐渐学习到的。
Final performance
我们用更长的时间训练一个更深的神经网络,其中包含40个残差单元。并将训练结果同其它程序作比较:AlphaGo Fan, AlphaGo Lee and several previous Go programs. We also played games against the strongest existing program, AlphaGo Master—a program based on the algorithm and architecture presented in this paper but using human data and features. We also included a player based solely on the raw neural network of AlphaGo Zero; this player simply selected the move with maximum probability. 结果如下图:
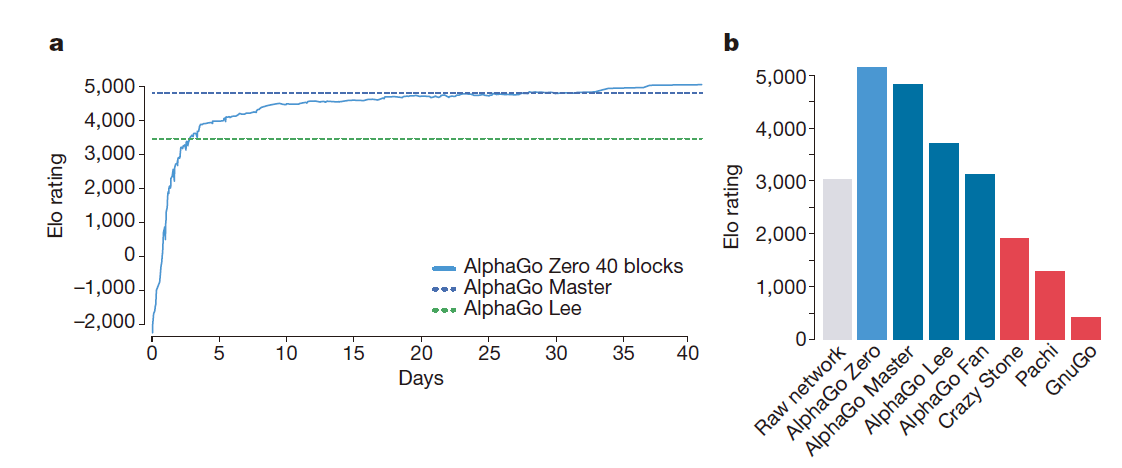
In the space of a few days, starting tabula rasa, AlphaGo Zero was able to rediscover much of this Go knowledge, as well as novel strategies that provide new insights into the oldest of games.
Methods
Reinforcement learning
策略迭代是一种经典的算法,它在策略评估和策略增强中间反复优化。AlphaGo Zero自对弈也可以被看成一个策略迭代方式,它采用MCTS同时作为策略增强和策略评估手段。Policy improvement starts with a neural network policy, executes an MCTS based on that policy’s recommendations, and then projects the (much stronger) search policy back into the function space of the neural network. Policy evaluation is applied to the (much stronger) search policy: the outcomes of self-play games are also projected back into the function space of the neural network. These projection steps are achieved by training the neural network parameters to match the search probabilities and self-play game outcome respectively.
Self-play RL
之前旧版的AlphaGo 采用一个网络评估价值,利用一个娴熟的结构,包括了连通性、领域,眼的围棋知识。这个网络利用TD-error学习。MCTS也可以看成一个Self-play RL的形式,并在之前的Go程序中取得了不错的成绩,但是用到了一定的领域经验:A fast rollout policy. 很多已有的算法都或多或少利用了“多余”的知识:比如利用SL初始化网络参数、某些人为选定的网络参数、人为限制行动区间、或者利用存在的程序产生训练样本等。Many of the most successful and widely used reinforcement learning methods were first introduced in the context of Zero-sum games: temporal-difference learning was first introduced for a checkers-playing program, while MCTS was introduced for the game of Go. 这些算法还被证明在很多其它的领域也很有作用。
Domain knowledge
下面展示了算法训练过程或者MCTS用到的所有的领域知识,在将算法迁移到其余马尔科夫类游戏的时候,这些信息需要更改:
- 提供了围棋的整套规则。这些规则用于MCTS返回状态和评分。游戏结束如果双方都pass或者下了$19\times19\times2=722$ 步。同时每一步我们都提供了合法的走子范围。
- AlphaGo Zero uses Tromp–Taylor scoring during MCTS simulations and self-play training. This is because human scores (Chinese, Japanese or Korean rules) are not well-defined if the game terminates before territorial boundaries are resolved. However, all tournament and evaluation games were scored using Chinese rules.
- The input features describing the position are structured as a 19 × 19 image; that is, the neural network architecture is matched to the grid-structure of the board
- 围棋的规则不会随着旋转或者对称改变。这个知识可以用于在训练时候增广数据,也可以在MCTS搜索的时候随机选择一个状态变化的形式(sample random rotations or reflections of the position during MCTS)。
除了上述知识之外,我们不再使用其它知识。比如我们没用rollout,同时所有的合法下子我们都是保留的(即使会填自己的眼)。算法的网络结构基于目前用于图像识别的算法。MCTS search parameters were selected by Gaussian process optimization, so as to optimize self-play performance of AlphaGo Zero using a neural network trained in a preliminary run.
Optimization
AlphaGo Zero players $\alpha_{\theta_i}$ are continually evaluated; and the best performing player so far, $\alpha_{\theta_\ast}$, is used to generate new self-play data. 每个mini batch 的数据都是从最近的 500,000 局自对弈数据中随机均匀抽样得到的。神经网络采用带动量的随机梯度下降法训练,the momentum parameter is set to 0.9. 并且这个学习速率也是随着训练逐步减小的。The cross-entropy and MSE losses are weighted equally (this is reasonable because rewards are unit scaled $r_T\in {-1,+1}$ ), L2正则项参数 c = 10−4. The optimization process produces a new checkpoint every 1,000 training steps. This checkpoint is evaluated by the evaluator and it may be used for generating the next batch of self-play games, as we explain next.
Evaluator
为了保证我们每次都能产生最佳的数据,在产生新数据之前,我们将每个新的checkpoint 同现在最佳的网络$f_{\theta_\ast}$ 对比。The neural network $f_{\theta_i}$ is evaluated by the performance of an MCTS search $\alpha_{\theta_i}$ that uses $f_{\theta_i}$ to evaluate leaf positions and prior probabilities. 每次评估包括400局对战,MCTS每次进行1600次仿真来选择动作,using an infinitesimal temperature τ→ 0 (that is, we deterministically select the move with maximum visit count, to give the strongest possible play). 如果新的网络赢率达到55%以上(为了避免噪声影响),那么新的网络就替代最佳的网络$f_{\theta_\ast}$ 用来选择动作,并成为下一次的比较对象。
Self-play
The best current player $\alpha_{\theta_\ast}$ is used to generate data. In each iteration,$\alpha_{\theta_\ast}$ plays 25,000 games of self-play, using 1,600 simulations of MCTS to select each move. 每场游戏开始的30步, 温度参数 τ = 1; 选择动作的概率正比于MCTS中的访问次数, 保证了探索的多样性. 余下来的步数, 温度参数采用无穷小, τ→ 0. 附加的探索通过添加 Dirichlet noise 到根节点 $s_0$ 的先验概率, $p(s,a)=(1-\epsilon)p_a+\epsilon\eta_a$, where $\eta \sim Dir(0.03)$ and ε = 0.25; this noise ensures that all moves may be tried, but the search may still overrule bad moves. 为了节约计算资源,明显输掉的比赛就应该提前终止。终止的阈值$v_{resign}$ 是自动选择的,保证the fraction of false positives (如果没有中断继续下子赢盘的概率)小于5%。而为了实现这个目标,我们每次都允许10%本来应该终止的棋局下完。
Supervised learning
为了对比,我们也通过监督学习训练了一个网络参数$\theta_{SL}$. The neural network architecture was identical to AlphaGo Zero. Mini-batches of data (s, π, z) were sampled at random from the KGS dataset, setting $\pi_a=1$ for the human expert move a. Parameters were optimized by stochastic gradient descent with momentum and learning rate annealing. The momentum parameter was set to 0.9, and the L2 regularization parameter was set to c = 10−4.
Search algorithm
AlphaGo Zero uses a much simpler variant of the asynchronous policy and value MCTS algorithm (APV-MCTS). 每个搜索树节点s包括了边(s,a) for all legal actions $a\in\mathit{A(s)}$ . 每个边都存有以下统计量:
Multiple simulations are executed in parallel on separate search threads. The algorithm proceeds by iterating over three phases, and then selects a move to play.
Select
the simulation reaches a leaf node at time step L(共走L步). At each of these time steps, t < L, an action is selected according to the statistics in the search tree,
where $C_{puct}$ is a constant determining the level of exploration; 一开始会倾向于先验概率更大的分支,后面逐渐倾向于action value更大的分支。$\sqrt{\sum_b N_r(s,b)}$ 表示父节点经过的次数,所以一定是大于1的(我们更新的时候先更新父节点再更新子节点,先更新Nr,再更新u(s,a))。
Expand and evaluate
The leaf node $s_L$ is added to a queue for neural network evaluation, $(d_i(p),v)=f_\theta(d_i(s_L))$, where $d_i$ is a dihedral reflection or rotation selected uniformly at random from i in [1..8]. Positions in the queue are evaluated by the neural network using a mini-batch size of 8; the search thread is locked until evaluation completes. 同时这步也会直接扩展叶子节点(因为现在评估和动作概率一起算了,所以肯定会扩展),每一条边$(s_L,a)$ 初始化为:
then the v is backed up.
Backup
The edge statistics are updated in a backward pass through each step t ≤ L. The visit counts are incremented, $N(s_t,a_t)=N(s_t,a_t)+1$, and the action value is updated to the mean value, $W(s_t,a_t)=W(s_t,a_t)+v,\; Q(s_t,a_t)=W(s_t,a_t)/N(s_t,a_t)$, We use virtual loss to ensure each thread evaluates different nodes.
Play
At the end of the search AlphaGo Zero selects a move a to play in the root position $s_0$, proportional to its exponentiated visit count, $\pi(a\mid s_0)=N(s_0,a)^{1/\tau}/\sum_b N(s_0,b)^{1/\tau}$, where τ is a temperature parameter that controls the level of exploration. 选择新的根节点并且将除新根节点以外的枝条都删除。AlphaGo Zero resigns if its root value and best child value are lower than a threshold value.
对比与旧版的MCTS,主要有以下区别:不再使用任何rollout;使用一个单一的策略和价值混合网络;leaf nodes are always expanded; 每一个搜索的线程简单地等待评估结束,而不是同时执行评估和backup; and there is no tree policy.
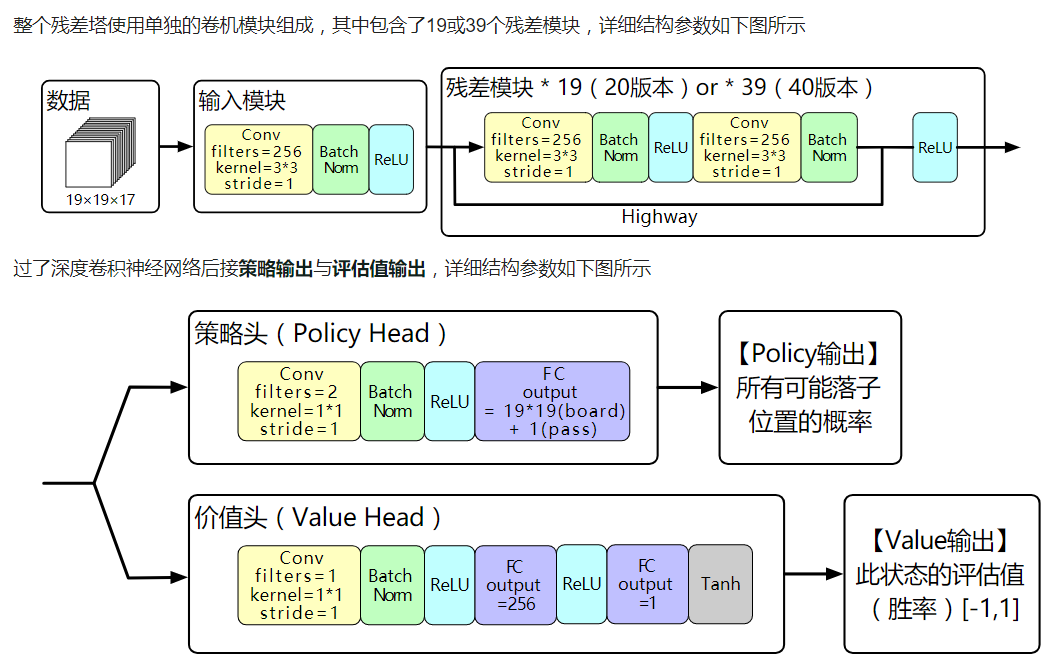
Neural network architecture
输入的参数是$19\times19\times17$ 的特征,全部采用one-hot编码:其中8个输入是我方最近8次下子的的棋盘形式(我方子地方为1,其余为0);再8个输入是对方最近8次下子的棋盘形式(对方下子地方为1,其余为0);还有一个全1或者全0的平面用于表征下棋的颜色(黑1白0),这个涉及到某些规则特殊性。输入表示如下:
网络结构如下图:
Datasets
The datasets used for validation and testing are the GoKifu dataset and the KGS dataset.
Conclusion
其实新版的算法和旧版的算法有很大的重合度,主要的改进在于loss function的定义,还有就是残差单元和联合网络的应用。值得注意的是,在自对弈的过程中,我们不再使用和中间训练过的网络对弈,而是采用最新网络自对弈。为了达到更好的训练效果,我们也增加了一定探索的策略。这个突破也说明了MCTS算法的有效性,我们也可以把它应用于其余方面。